Distributed ledger technology and its regulation
What is distributed ledger technology?
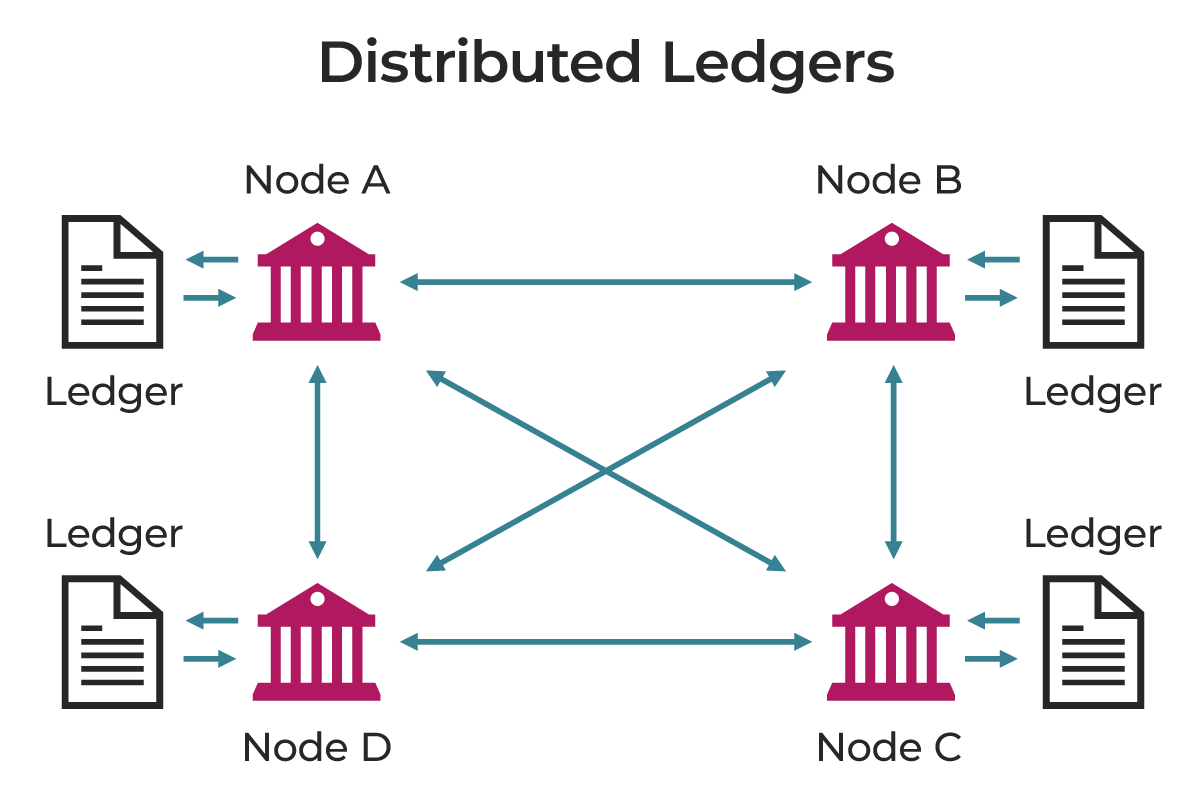
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) is a technology that uses independent computers, referred to as nodes, to record, share, and synchronise transactions with their respective electronic recording units. It differs from the traditional data recording mainly because the data are not centralised but decentralised and connected with cryptographic elements.
DLT is a technological infrastructure and protocols that enable simultaneous access, validation, and updating of records in a networked database. DLT is the technology from which blockchains are built. This infrastructure allows users to view all changes, identify the responsible parties, reduces the need for data auditing, ensures data reliability, and restricts access to authorised personnel.
How does distributed ledger technology work?
DLT ensures the secure and accurate storage of information using cryptography. Data is accessed through keys and cryptographic signatures. Once saved, the data forms a permanent database. The distributed ledger operates based on network rules embedded in the database's programming code.
Distributed ledgers are maintained by a network of nodes each of which possesses a copy of the ledger for validating information and achieving consensus on its accuracy.
Nodes serve as the backbone of the blockchain network, primarily verifying transactions and upholding ledger accuracy. When a transaction occurs on the blockchain, it is broadcast to all network nodes.
Blockchain technology vs distributed ledger technology
Blockchain technology is a specific form of DLT, where data is organised into blocks that are linked together in a chain. DLT is a broader term that refers to any technology that distributes data across multiple nodes without a centralised authority. The use of blockchains often involves additional elements, such as consensus algorithms and the execution of smart contracts, to maintain network security and functionality. All blockchains are distributed ledgers, but not all distributed ledgers are blockchains.
Blockchains are unique in that they provide an immutable chain of entries, whereas other DLTs may offer more flexible data management options. The blockchain technology is often associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. In contrast, DLT can be applied more broadly across various corporate and public sectors.
Crypto-assets are among the primary applications of blockchain technology and DLT within the financial sector.
A pilot regime on DLT for market infrastructures
Regulation (EU) 2022/858 of the European Parliament and of the Council on a pilot regime for market infrastructures based on distributed ledger technology was adopted on 30 May 2022. The pilot regime is the so-called sandbox approach or a controlled environment which allows for temporary exemptions from the existing provisions to enable financial regulators to gain experience with the use of DLT in market infrastructures, while ensuring that they can prevent risks to ensure investor protection, market integrity, and financial stability.
To implement the Regulation on a DLT pilot regime, Section 3 of the Financial Instrument Market Law was amended to include a reference to this regulation and to expand the list of the financial instruments to include those issued using the DLT.
The DLT pilot regime aims to facilitate the development of crypto-assets, qualified as financial instruments, and DLT, while maintaining a high level of investor protection, market integrity, financial stability, and transparency, as well as preventing regulatory arbitrage and potential shortcomings.
The DLT users under the pilot scheme will follow the users licensed by the European Union (EU):
- investment firms and market operators that will be able to apply for authorisation to organise and maintain a DLT multilateral trading facility;
- central securities depositaries that will be able to apply for authorisation to maintain the DLT settlement system.
The pilot regime also provides a new, non-traditional type of market infrastructure, the DLT trading and settlement systems, which will combine both the DLT multilateral trading facility and the services provided by the DLT settlement system. The DLT trading and settlement systems must be either a DLT multilateral trading facility organised by an investment firm or a market operator authorised to organise and maintain the DLT trading and settlement systems or a DLT settlement system maintained by the central securities depository authorised to maintain the DLT trading and settlement systems.

